A Beginner’s Guide to Bookkeeping Basics 101
Bookkeeping can seem overwhelming, especially with all the demands of running a small business. Mastering bookkeeping basics is easier than you think, and we’re here to guide you through it, ensuring your accounts are organised, up to date and accurate.


Bookkeeping Definition
Small Business bookkeeping is recording and organising a business’s financial transactions. It involves tracking income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity to create a clear and accurate picture of the company’s financial position.
It is the foundation of your financial records, providing essential data for decision-making, tax preparation, and overall business management.
Bookkeeping vs Accounting
Bookkeeping is the first step in managing your finances. It involves organising receipts and bills and recording every penny that comes in and goes out of your business.


Accounting is the process of analysing receipts and bills to create a bigger picture of your finances. Accountants use the information bookkeepers gather to prepare reports, analyse trends, and offer advice to help you make better business decisions.
In short, bookkeeping is the recording of financial data, while accounting is the interpretation and analysis of that data.
Bookkeeping Basics Terms
Here are some basic bookkeeping terms you might come across to help you get started.
- Assets: What your business owns (e.g., cash, inventory, equipment).
- Liabilities: What your business owes (e.g., loans, unpaid bills).
- Equity: The value of your business after liabilities are deducted from assets.
- Income: Money your business earns (e.g., sales, services, interest).
- Expenses: Costs incurred to run your business (e.g., rent, salaries, supplies).
- Profit: The amount left over after expenses are deducted from income.
- Loss: When expenses exceed income.
- Invoice: A bill sent to a customer for goods or services.
- Receipt: Proof of payment for goods or services.
- Double-Entry Accounting: A system where transactions are recorded in two accounts (a debit and a credit).
- Ledger: A book or digital record where a business’s financial transactions are organised and summarised by account.
- Chart of Accounts: A list of all the accounts used to record financial transactions.
- Reconciliation: The process of comparing your records with bank or credit card statements to ensure accuracy.
- Financial Statements: Reports summarising your business’s financial performance (e.g., balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement).
For a complete list, see our bookkeeping and accounting terms.
Setting Up Your Bookkeeping System
As a small business owner, there are a few decisions to make before starting business bookkeeping.
Accrual vs Cash Accounting Method
You will need to choose the best accounting method for your business.
Accrual Accounting
Accrual accounting is a method of recording financial transactions based on recognising income and expenses when they occur rather than when cash is exchanged. This approach accurately represents a company’s financial position, reflecting all relevant activities and events during a given period. Accruals are posted to the balance sheet.
Cash Accounting
Cash accounting is a simple method of managing finances for small businesses. It only records transactions when cash is exchanged, providing an accurate picture of current cash flow. This type of accounting is beneficial for small businesses and self-employed as it allows for easier tracking of expenses and income.
Separate business Bank Account
A separate business bank account simplifies your bookkeeping by keeping business transactions distinct from personal ones. It also makes a small business appear more professional and trustworthy.
If you are starting a Limited company, you must use business bank accounts because it is a separate legal entity. A business bank account can offer loans, overdrafts, free tools, and advice.
Many banks offer business banking. It is essential to examine what they offer and whether there is free banking.
Recording Financial Transactions
There are several ways to complete the bookkeeping. Depending on your skills and the size of the business will depend on the best option.
Paper Records or Ledger Books
A ledger book is a physical record book where you manually enter every financial transaction. It typically includes columns for the date, description, and amounts for debit and credit entries.
- Pros: Simple and straightforward, requires no special software or technology.
- Cons: Time-consuming, prone to human error, difficult to search and analyse data.
Microsoft Excel
Excel spreadsheets offer a more flexible and convenient way to record business transactions digitally. You can create custom templates, formulas, and charts to organise and analyse your financial data.
- Pros: Relatively easy to use, familiar for many, allows for customisation and calculations.
- Cons: It can become complex quickly, requires some spreadsheet knowledge, and has the potential for formula errors.
We have created a basic bookkeeping template to record your income and expenses for the year.
See also our list of other helpful bookkeeping templates.
Accounting Software (Streamlined Solution):
Accounting software solutions like Xero, QuickBooks, or FreshBooks automate many bookkeeping tasks, making recording business transactions, financial reporting, and reconciling accounts easier.
- Pros: It is efficient and accurate, offers a wide range of features, and often includes cloud storage for easy access.
- Cons: It can be more expensive than other options and may require a learning curve for new users.
Top Tip: When choosing the best way to record financial transactions, look at the long term to see if your choice is suitable if the business expands. Accounting software can grow with your business.
Basic Bookkeeping Tasks
There are many bookkeeping tasks to keep your income and expenses up to date, including:
Create Sales Invoices
A sales invoice is a document a seller issues to a buyer to request payment for goods or services. It provides a record of the sale for both the seller and buyer. Invoices can be created by hand, using an invoice template, or using accounting software.
Sales invoices should be issued promptly and accurately. This ensures that the records are up to date and that you have legal proof of the business transaction.
Accounts Payable
Learn how to record purchase invoices, run the accounts payable ledger, file supplier invoices, and manage your cash flow. The Accounts payable shows how much a small business owes to its suppliers.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts Receivable refers to the money customers owe for goods or services provided on credit. In other words, the money has been billed but not yet paid. Accounts receivable are considered assets on a company’s balance sheet, representing future cash flow for the business.
A good credit control system to collect unpaid invoices is essential for a good cash flow. Accounting software can send invoices, chase outstanding amounts, send statements and produce reports.
Bank Reconciliation Basics
Completing a bank reconciliation ensures that all the transactions from the bank statements appear in the accounting system. Learn the basics of bank reconciliation, why it is essential, and how to complete it.
Business Expenses
Ensure you claim all business expenses incurred; this will reduce your profits and, therefore, your tax liability. Business expenses include mileage and anything that you pay for personally related to business operations. Use our free template.
Financial Statements
Producing financial statements is crucial for any business as part of bookkeeping basics. These statements provide a snapshot of your company’s financial health and performance over a specific period. The three main financial statements are:
- Balance Sheet:
This statement gives you a snapshot of your business’s financial position at a specific point in time. It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the owner’s equity (the difference between assets and liabilities).
- Income Statement:
Also known as the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, this report details your business’s revenues and expenses over a specific period. It shows whether your business is making a profit or incurring a loss and how much. Think of it as a performance report card for your business.
- Cash Flow Statement:
This statement tracks the cash flow in and out of your business during a specific period. It highlights how your business generates and uses cash, which is vital for understanding your liquidity and ability to meet financial obligations. Consider this a map of your cash flow, revealing where money is coming from and where it’s going.
Payroll
Not all small businesses need a payroll system, but if they do, it can be outsourced to a payroll bureau, completed by an accountant or bookkeeper, or used with accounting software like QuickBooks, which offers the feature for a small monthly fee.
Small Business Bookkeeping Basics Tips
Here are our top tips on bookkeeping:
- Separate Business and Personal Finances: Open a dedicated business bank account and credit card to avoid confusion and simplify record-keeping.
- Set up a bookkeeping process: Depending on the type and size of the business will depend on the processes you put in place. Look at all aspects of bookkeeping to find the best process.
- Track Every Penny: Record every income and expense, no matter how small. This will give you a clear picture of your cash flow.
- Keep Organised Records: Create a system for storing receipts, invoices, and bank statements. Digital storage solutions like cloud-based apps can be helpful.
- Reconcile Regularly: Compare your records with bank and credit card statements monthly to catch errors early.
- Categorise Transactions: Use a chart of accounts to categorise income and expenses. It will help you track spending patterns and identify areas for improvement.
- Choose the Right Tools: Whether you use a simple spreadsheet or accounting software or hire a professional bookkeeper, choose tools that suit your needs and budget.
- Stay on Top of Taxes: Set aside money for taxes throughout the year to avoid a big bill at the end. Consult a tax professional for guidance on deductions and compliance. Ensure you submit tax returns on time.
- Review Financial Statements: Regularly review your balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to monitor your business’s financial health.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Ask for Help: If you feel overwhelmed or confused, don’t hesitate to seek help from a bookkeeper or accountant. They can provide expert guidance and save you time and money in the long run.
- Make It a Habit: Schedule regular time for bookkeeping. Even a few minutes daily can make a big difference in staying organised and controlling your finances.
Bookkeeping Examples
We have produced many bookkeeping examples to help you understand the basics. These include posting the double entry to sales, purchases, equity, depreciation, prepayments, and accruals.
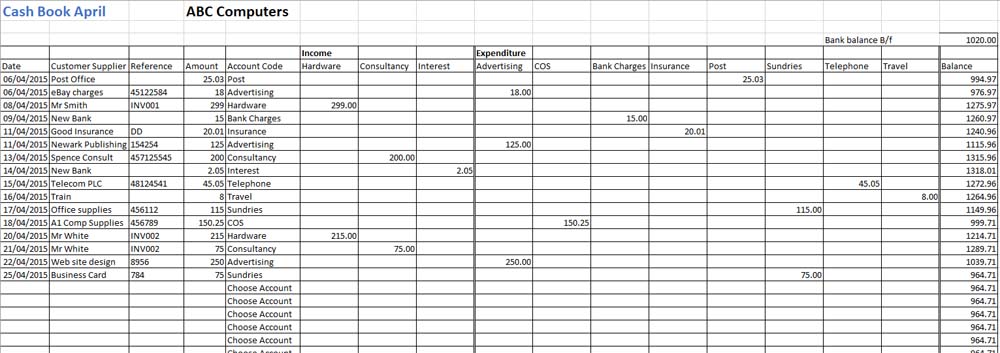
We also have an example of our simple-to-use cashbook; it is available to download.

How to Become a Bookkeeper
Starting your own bookkeeping business can be rewarding for those with a knack for numbers and a passion for helping small businesses thrive. With the right skills, knowledge, and dedication, you can offer valuable financial services to entrepreneurs who need help managing their books.
Launching a bookkeeping business requires careful planning, including deciding on your niche, setting up a business entity, obtaining necessary licenses, and choosing the right bookkeeping software and tools to streamline your operations.
Bookkeeping Courses
If you want to learn more about bookkeeping and accounting, many courses are available, from simple online introductions to fully qualified bookkeepers. Please read our guide on bookkeeping courses.
Bookkeeping Basics Conclusion
Mastering basic bookkeeping is fundamental to ensuring your small business’s financial health and long-term success. By diligently tracking your income and expenses, staying organised, and utilising accounting software, you’ll understand your financial situation clearly, empowering you to make informed decisions and plan for the future.
Bookkeeping doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With a little effort and the knowledge you’ve gained from this guide, you can confidently manage your business finances and pave the way for a prosperous future.






